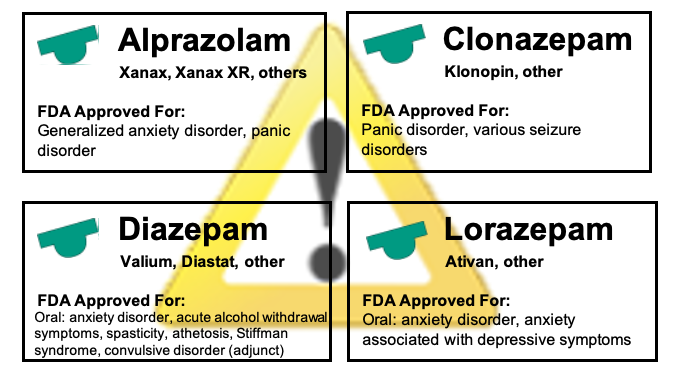
When comparing Ativan (lorazepam) to Xanax (alprazolam), Valium (diazepam), and Klonopin (clonazepam), it’s essential to consider factors such as onset of action, duration, potency, and specific indications to maximize efficacy for a particular condition.
1. Onset of Action
- Ativan: Intermediate onset; takes about 20-30 minutes.
- Xanax: Rapid onset; usually within 15-30 minutes.
- Valium: Very rapid onset; within 15 minutes.
- Klonopin: Slower onset; takes 30-60 minutes.
2. Duration of Action
- Ativan: Short to intermediate duration (6-8 hours).
- Xanax: Short duration (4-6 hours).
- Valium: Long duration (up to 24 hours).
- Klonopin: Long duration (12 hours or more).
3. Potency
- Xanax: Considered highly potent and very effective for acute anxiety or panic attacks.
- Ativan: Potent and versatile; effective for both anxiety and insomnia.
- Valium: Less potent but long-acting, making it suitable for anxiety, muscle spasms, and alcohol withdrawal.
- Klonopin: Very potent and effective for seizure disorders and panic disorder.
4. Indications
- Ativan: Often prescribed for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), short-term treatment of insomnia, and for sedation.
- Xanax: Primarily used for panic disorder and short-term management of anxiety.
- Valium: Used for anxiety disorders, muscle spasms, seizures, and alcohol withdrawal.
- Klonopin: Mainly prescribed for seizure disorders and panic disorder.
5. Side Effects and Dependence
- Ativan: Known for its lower risk of dependence compared to Xanax. However, prolonged use can still lead to dependence and withdrawal issues.
- Xanax: High potential for dependence, especially with long-term use. Abrupt discontinuation can cause significant withdrawal symptoms.
- Valium: Lower risk of dependence due to its long half-life, but withdrawal can be prolonged.
- Klonopin: Less risk of dependence compared to Xanax but still significant with long-term use.
Maximizing Efficacy
- For Acute Anxiety: Xanax may be the most effective due to its rapid onset and potency, but careful consideration of the risk of dependence is needed.
- For Insomnia or Short-Term Sedation: Ativan is often preferred due to its intermediate onset and duration, offering efficacy with a lower risk of next-day drowsiness.
- For Long-Term Anxiety or Conditions with Seizures: Klonopin or Valium might be more appropriate due to their longer duration of action and less frequent dosing requirements.
- For Alcohol Withdrawal: Valium is often the drug of choice due to its long half-life and muscle relaxant properties.
Conclusion
Choosing between these medications should be based on specific symptoms, the duration needed, and individual response to the medication. Ativan is versatile and has a balanced profile, but Xanax may be more effective for rapid relief of severe anxiety. Valium and Klonopin offer longer-lasting effects and are better suited for long-term management.
Would you like to explore more on how to use these medications safely or how they compare in terms of withdrawal and dependence?